Money tips for everyday life
What is APR? A Simple Guide to Understanding Annual Percentage Rate
What is APR?
APR, or Annual Percentage Rate, is the yearly cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage, and includes interest and certain fees (like loan origination fees) depending on the type of credit. For credit cards, APR typically doesn’t include some fees like annual or late fees.
APR, or Annual Percentage Rate, helps you compare loans and credit cards by showing the true cost of financing over time. If you've ever applied for a credit card, taken out a loan, or financed a big purchase, you've probably come across the term "APR," but what exactly does it mean for you? Let’s break it down.

What Is APR?
In simple terms, APR stands for Annual Percentage Rate and it is the yearly cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage. APR includes interest and can include certain fees (like loan origination fees) depending on the type of credit you obtain, though for credit cards, it typically doesn’t include all certain fees like annual or late fees. A lower APR generally means lower borrowing costs, while a higher APR means it will cost more to carry a balance or repay the loan. APR gives you a clearer picture of what you're actually paying when you borrow money, making it easier to compare different loan or credit offers.
What Is the Difference Between APR and Interest Rate?
APR and interest rates are different, but a common misconception is that they mean the same thing. While they’re related, APR and interest rates are not identical. Take a look at the breakdown below to understand how these two terms differ:
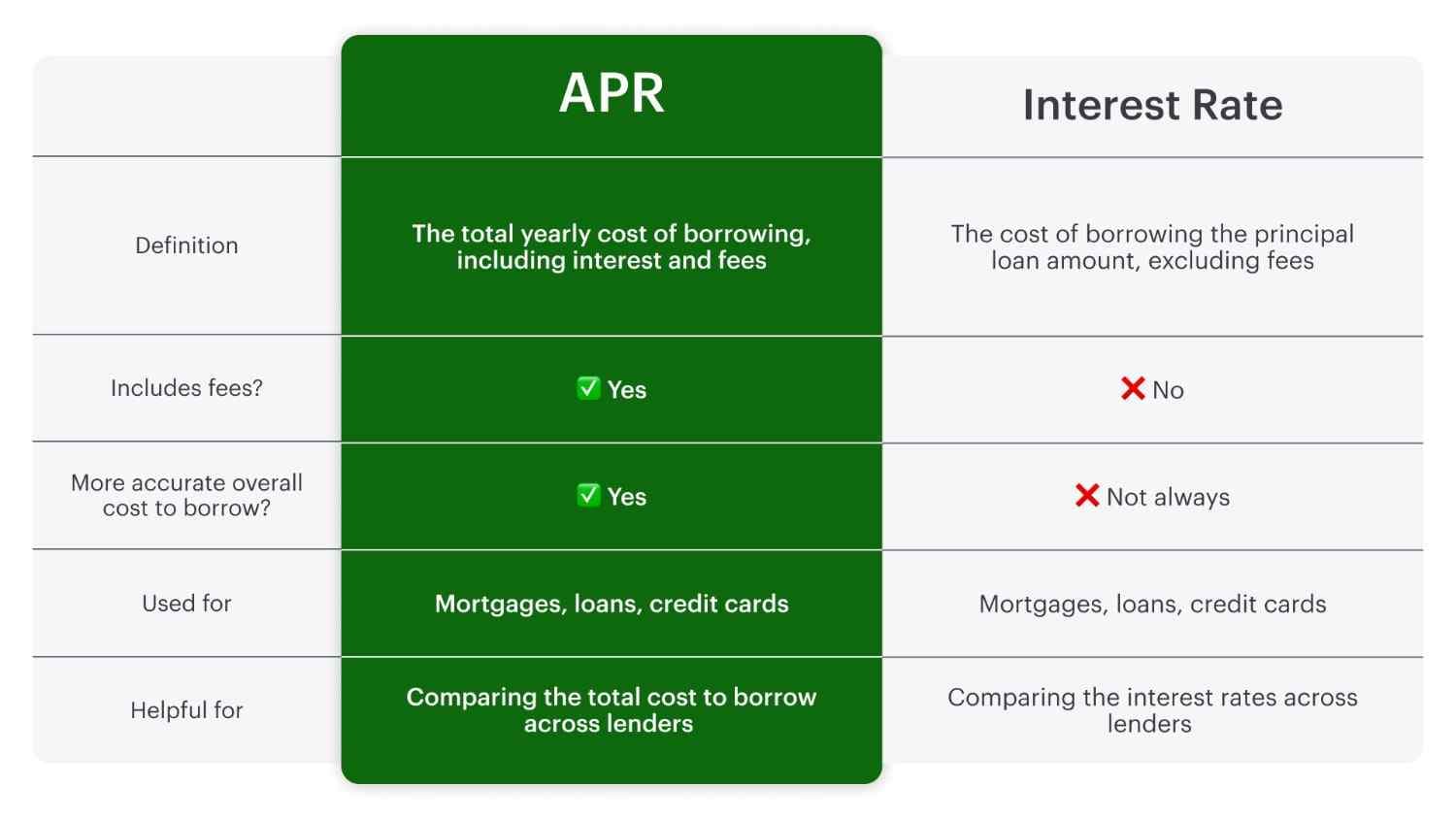
Think of APR as the “all-in” cost of borrowing credit. If you're comparing two offers, the one with the lower APR may cost less in terms of fees incurred or balances held over time if all other factors are equal.
Types of APR
The definition of APR can vary depending on the type of credit you’re using. Here are a few common types:
- Fixed APR: Stays the same over time, making it easier to predict your payments
- Variable APR: Can change based on market interest rates, which means your cost of borrowing could change with the market
- Introductory APR: A special promotional rate offered for a limited time when you open a new credit card
- Penalty APR: A higher rate that kicks in if you miss payments or violate your credit terms
APR Explained: Why It Matters
Understanding APR is essential because it directly affects how much you’ll pay to borrow money. It also helps you understand long-term costs; a lower APR generally means you’ll pay less over time. Finally, APR can impact your financial goals, and lower borrowing costs mean more money stays in your pocket. Whether you're choosing between credit cards, personal loans, or auto loans, APR helps you compare offers apples-to-apples.
How to Use APR to Your Advantage
Here are a few smart ways to use APR when managing your finances:
- Shop around: Don’t take the first offer and compare APRs from different lenders to find the best deal
- Improve your credit score: A higher credit score may qualify you for lower APRs
- Read the fine print: Some lenders advertise low APRs that only apply under specific conditions or for a limited time
- Pay off high-APR debt quickly: The higher the APR, the more interest you’ll rack up over time
APR Bottom Line
APR may look like just another financial acronym, but it plays a big role in your borrowing decisions. APR helps you compare loan and credit card offers by showing the true cost of financing over time. Whether you're taking out a loan or signing up for a new credit card, understanding APR can help you make smarter, more informed choices and save you money in the long run.
Next time you see APR on a loan offer or credit card ad, you’ll know exactly what it means and how to spot a good deal when you see one.